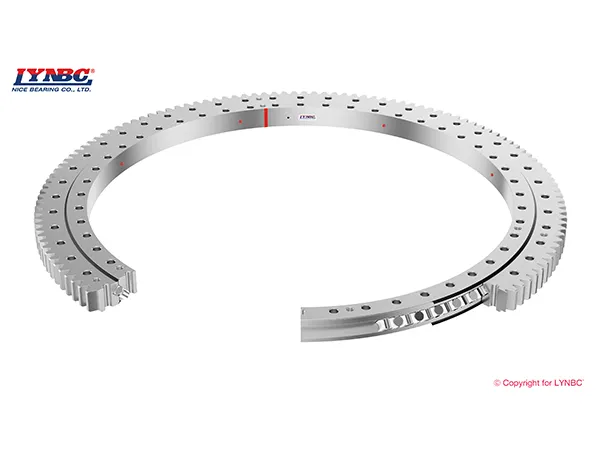
Four Point Contact Ball Slewing Bearing
A four-point contact ball slewing bearing is a type of rolling element bearing designed to handle axial, radial, and moment loads simultaneously. It features a single row of balls and an inner and outer ring, with a unique raceway geometry that allows the balls to make contact at four points.
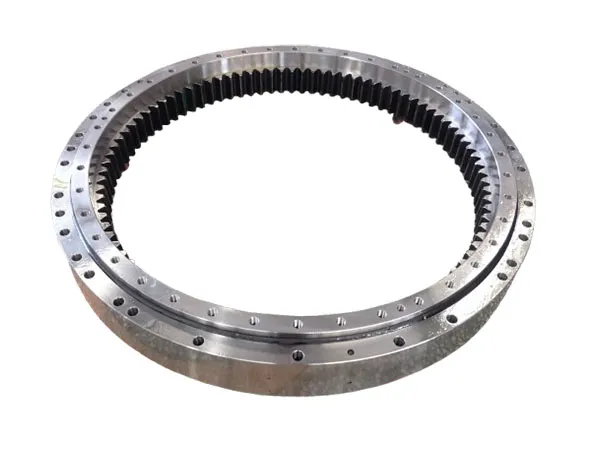

Double-row Ball Slewing Bearing
The double-row ball slewing bearing is a specialized type of slewing bearing designed to handle high axial and radial loads, as well as tilting moments. It features two rows of ball bearings arranged in a compact structure, enhancing load-carrying capacity and rotational stability.This type of bearing is commonly used in heavy-duty applications such as cranes, excavators, wind turbines, and material handling equipment. Its design allows for smooth and precise rotation, making it ideal for machinery that requires reliable and efficient movement.
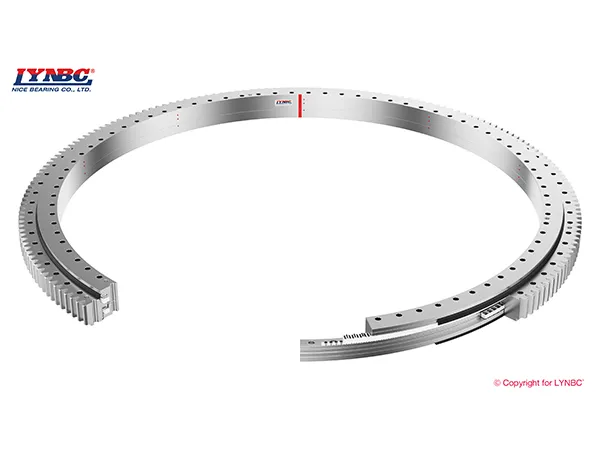
Three-row Cylindrical Roller Slewing Bearing
A three-row cylindrical roller slewing bearing is a specialized bearing designed for extremely demanding applications where high load capacity, rigidity, and precision are paramount. While they offer significant advantages in these areas, they are also more expensive and require more careful consideration during the design and installation process.
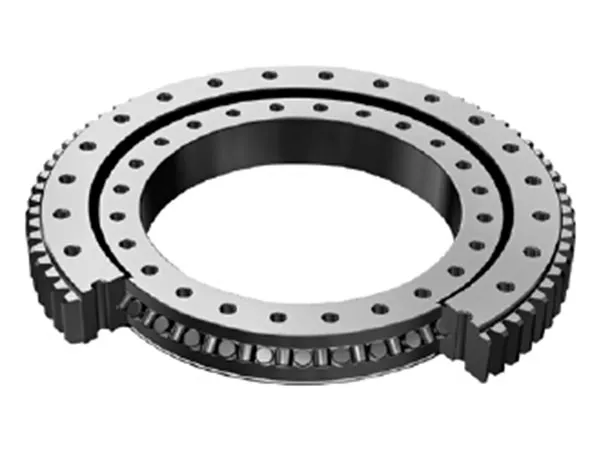

Cross Cylindrical Roller Slewing Bearing
Cross cylindrical roller slewing bearings are a powerful solution for applications requiring high load capacity, precise rotation, and compact design. Careful consideration of the selection criteria is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Configure
The slewing bearing, also called a turntable bearing, can be provided with various types and sizes of holes. Also, it is available in different configurations, such as internal gear, external gear, and gearless types. Special double row and triple row configurations are also provided so as to meet individual demands.
Structures
The slewing bearing is a basic part for transmitting mechanical force between two parts on equipment that need relative rotation under the axial force,radial force and tilting moment at the same time. lt is often fastened on the upper and lower supports of the mechanical equipment by bolt. Designed with mounting holes, internal or external gear, lubricating holes and sealing device, this type of rolling element bearing owns compact structure with high rigidity. It features light weight, steady operation, high precision, safety and other characteristics.
Application
Involved in a large range of applications, the slewing bearing is a commonly seen bearing for construction machinery. To illustrate, it is often applied on cranes, cement pump track, road roller. wind turbine, solar power generating equipment. tidal power equipment, ship unloading machine, ladle turret, stacker-reclaimer, radar tank, satellite launcher, ferris wheel, CT machine, and more. In addition, our slewing bearing has a wide customer base in China and other countries, like America,Germany, India,South Korea, Japan,Singapore, Peru,ltaly, etc.
Type
We can provide many kinds of slewing bearings, such as :
1. Four point contact ball slewing bearings;
2. Double-row ball slewing bearings;
3.Three-row cylindrical roller slewing bearings;
4. Crossed roller slewing bearings;
5.INA Crossed roller slewing bearings;
6.INA Light Series Four point contact ball slewing bearings;
7.INA Four point contact ball slewing bearings.
Customizable
As a professional slewing bearing manufacturer in China, we can produce slewing bearings of different sizes, from small size (D=300mm) to large size (D=120000mm), including internal gear, external gear, no gear and other types.
Technical Support
We can also provide consultation for customers as well as design specific slewing bearing according to your requirements. Meanwhile, we also provide thrust bearings, roller bearings, angular contact ball bearings, deep groove ball bearings and other bearings. lf you are in need of slewing bearings or other bearings, please contact us.
Visual Checks
Look for cracks, corrosion, or damage on the bearing surface.
Inspect the seals for wear, tearing, or missing sections.
Ensure that bolts are tight and not loose or broken.
Lubrication Check
Verify the presence and condition of lubricant.
Check for contamination (dirt, metal particles, or water in the grease).
Rotation & Noise Monitoring
Slowly rotate the bearing and listen for abnormal noises (grinding, knocking).
Feel for irregular resistance or stiffness.
Grease Type & Interval
Use the manufacturer-recommended grease (typically lithium-based for general applications).
Apply fresh grease every 100-200 hours of operation or as recommended.
Lubrication Process
Inject grease evenly into all grease points while rotating the bearing slowly.
Wipe off excess grease and check for leakage.
Ensure new grease pushes out old grease and contaminants.
Regularly check bolt torque using a torque wrench.
Retighten bolts per the manufacturer’s torque specifications.
Replace any damaged or loose bolts immediately.
Keep seals clean and free from debris.
Replace damaged seals promptly to prevent contamination.
Apply a protective coating if exposed to harsh environments.
Avoid exceeding the maximum load capacity.
Ensure proper load distribution to prevent premature wear.
Avoid shock loads or excessive vibrations.
Keep the area around the bearing free from dirt and debris.
If not in use for a long time, apply a protective coating or cover.
Use a dial indicator to check axial and radial movement.
Compare results to manufacturer’s allowable limits.
Replace the bearing if wear exceeds safe limits.
Maintain a log of inspections, lubrication, and repairs.
Track any performance irregularities for early issue detection.
If you are interested in our products and services,
please feel free to contact us!
Get in tuch

+86-379-60689957
Lianmeng Road, Jianxi district, Luoyang City,Henan province.